Full desalination
EFFICIENT FULL DESALINATION THROUGH MIXED BED CARTRIDGES OR ELECTRODEIONISATION
The conductivity achievable by reverse osmosis systems is not sufficient for complete water desalination. For this reason, reverse osmosis systems are either followed by mixed bed cartridges or electrodeionisation (EDI) systems. It is also possible to use systems with cation exchangers, anion exchangers and trickle degassers. The resin in these systems must be regenerated with acids or alkalis. Due to the effort involved and the safety conditions, this system technology is only used in project areas. The lowest conductivity values can be achieved with electrodeionisation systems.
MIXING BED CARTRIDGES
Mixed bed cartridges for complete desalination using combined ion exchange resins
Mixed bed cartridges
Mixed bed cartridges contain a mixture of cation and anion exchange resin, which can be used to remove all ions from the water. The conductivity values are measured. The functionality of mixed bed cartridges is maintained by regeneration through resin replacement when the conductivity limit is reached.
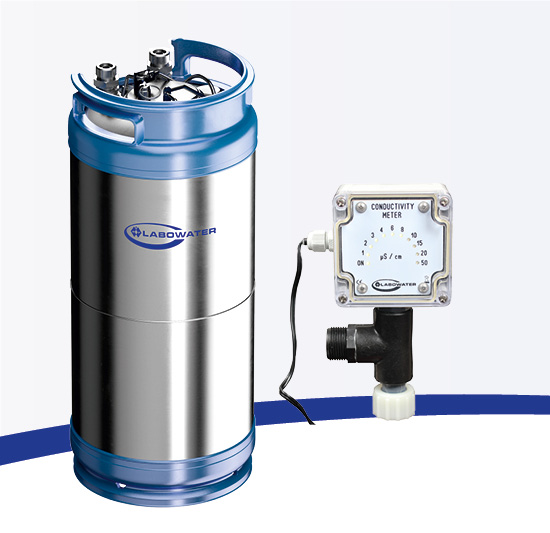

Labowater DM
Ion exchanger cartridge made of pressure-resistant stainless steel, filled with regenerable mixed-bed resin, connection: R ¾" AG
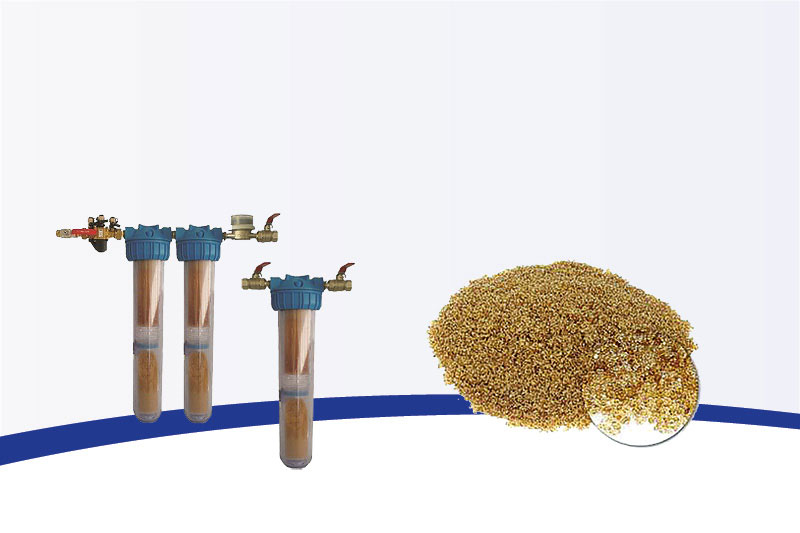

HAS Combi VE make-up water system
System for supplying small heating circuits with fully demineralised water; colour change when resin is exhausted, ¾" female thread version
Regeneration
Regeneration of ion exchanger cartridges from all manufacturers with mixed bed resin filling, various sizes can be filled on site as part of route planning.
ELECTRODEIONISATION (EDI)
Electrodeionisation for the production of pure water with particularly low conductivity
Electrodeionisation (EDI)
If higher demands are placed on the conductivity of pure water (dilute), it is possible to achieve conductivity values < 0.1 µS/cm using an electrodeionisation system. The structure and function of an electrodeionisation cell are shown in the image below. A reverse osmosis system is required for pre-treatment. An electrodeionisation system consists of cells that are separated from each other by semi-permeable membranes against cations and anions and filled with ion exchange resin. Applying an electrical voltage to the opposite plates ensures that the cations migrate through the cation-impermeable membrane to the negative pole of the voltage pole and the anions migrate through the anion-impermeable membrane to the positive pole of the voltage pole. The applied voltage also causes water molecules to dissociate into H+ and OH-. With the help of the H+ and OH- ions, continuous regeneration of the mixed bed resin takes place without the usual use of chemicals. Excess H+ and OH- ions can recombine to form water.
The electrodeionisation systems are designed for the respective application. Take advantage of the optimal service for our entire product range!
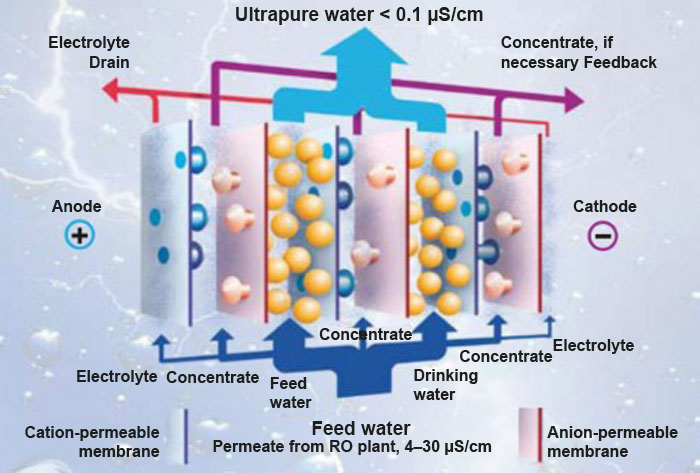
Structure and functional diagram of an electrodeionisation (EDI) system
 DE
DE  EN
EN 