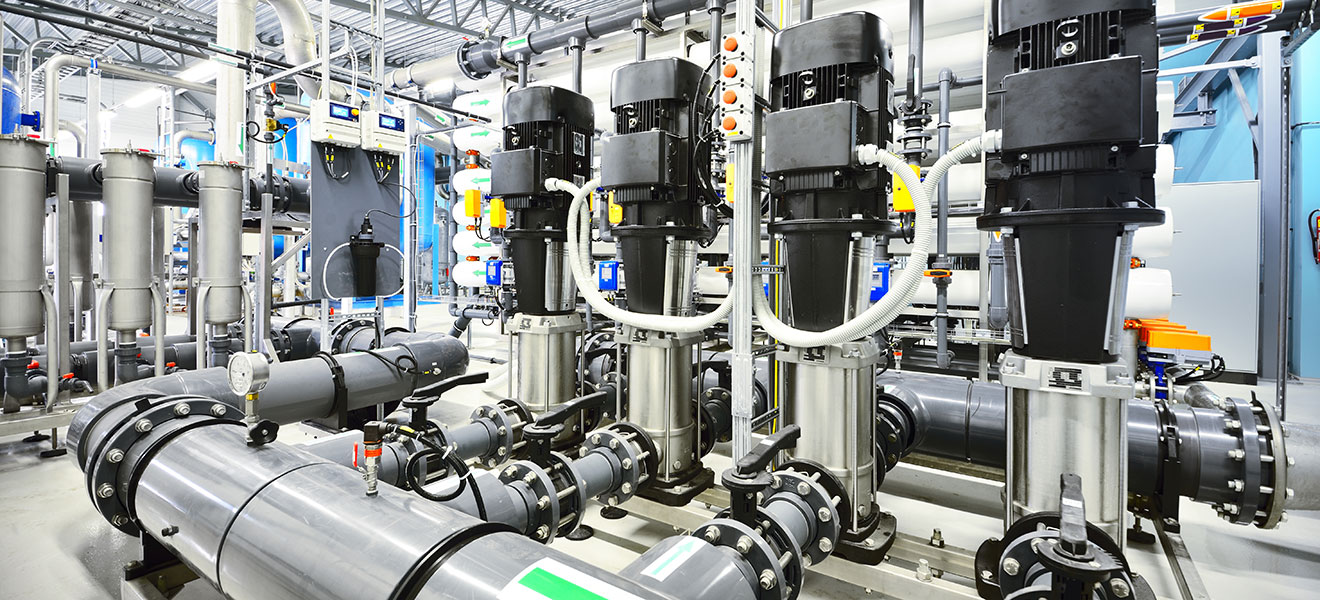
Reverse osmosis – a highly efficient membrane process for water treatment
Reverse osmosis is a modern water treatment process that effectively removes impurities using semi-permeable membranes. Water is forced through the membrane under pressure, which retains salts and pollutants.
1. What is reverse osmosis?
Reverse osmosis is the technological reversal of the natural osmosis process. A semi-permeable membrane separates liquids with different salt contents. Pressure is applied to push water from the side with a high salt content to the side with a low salt content.
2. Functionality and components
The resulting, almost salt-free water is called permeate and is collected in a container. The remaining concentrate or retentate contains the enriched salts and is usually discarded or used for other purposes. Reverse osmosis systems consist of several membranes, a high-pressure pump and a control unit.
3. Salt retention and performance
Salt retention varies between 92.0% and 99.7% depending on the membrane type and manufacturer. 100% retention is not possible due to manufacturing tolerances, as small amounts of monovalent ions in particular can enter the permeate.
4. Protection and pre-treatment of membranes
To protect the membranes from damage, careful pre-treatment of the feed water is necessary. Carbonates and sulphates often cause the membrane to become ‘blocked’. Water softeners remove such hardness components, which are monitored by a residual hardness control device . In addition, fine filters and, in the case of chlorinated water, activated carbon filters ensure the removal of colloids, biological substances and particles.
5. Operation and efficiency
The permeate usually leaves the membrane without pressure and is collected in a germ-proof sealed container. Since the pressure must be increased for further use , a pressure booster pump is used. Standard systems achieve a yield of around 75%, which can be increased to up to 92-94% through special retentate treatment .
6. Conclusion
Reverse osmosis systems are one of the most important and effective membrane processes for water treatment today. Through continuous maintenance and pre-treatment of the membranes, they ensure high water quality and are indispensable for many industrial and private applications.
 DE
DE  EN
EN 
